Network switch

A network switch can expand the number of available network ports. One router often does not have enough ports available. Connect a switch to the router to get more network ports.
On this page we tell you what to look out for when buying a switch. In addition, we provide many options of switches with different features.
Best (most speed)
Some switches can do more than just connect computers to a network. For example, Quality of Service (QoS) can significantly reduce latency (lag / delay) by prioritizing certain traffic. This improves the quality of real-time applications, such as online gaming and voice-over-IP (VoIP).
The best switches not only offer fast gigabit ports, but also have features such as Denial-of-Service (DoS) protection, Access Control Lists (ACLs), performance monitoring and VLANs.
These switches are not only fast, but also have many additional functions to improve the network:


With wifi (wireless)
Sometimes it is useful to combine a wifi access point with a switch. However, that is not a function of switches.
If you are not using the WAN port on a wifi router, it is actually a switch with wifi. Make sure to disable DHCP on the router.
In addition, they often also have all kinds of useful extra functions:
Rackmount (enterprise)
Enterprise switches often have 16, 24 or even 48 ports available. These are good switches with 16 and 24 ports:
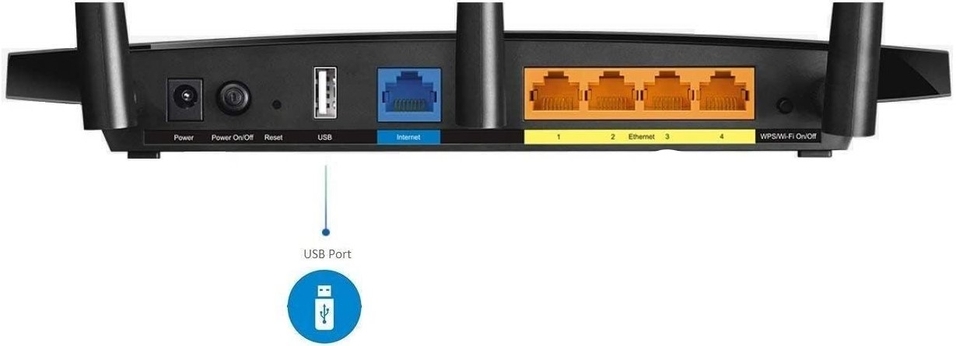
With USB port
Do you want to connect a hard drive or printer to the home network? Some routers also have a USB port, with which you can easily share these devices with all computers over the network.
However, this feature is not provided by switches, but routers. These routers have both a built-in network switch and a USB port:
With PoE (Power over Ethernet)
Many switches can also supply power through the network cables. This is called Power over Ethernet. For example, if you install an IP camera system, the camera can receive power via the network cable. The camera then no longer needs a power outlet.
For this to work, both devices must support power over Ethernet.
It is indicated on this page whether PoE is supported on the switch shown.
Small (mini)
Switches start from 5 ports. These network switches therefore have the smallest size. They can be easily placed on a desk.
Cheap
Often a simple switch already meets the requirements of many households. These are simple gigabit switches without additional functions:
What is a network switch?
You can connect computers to a network with a switch. The router that you get from the ISP often does not have enough ports for all devices in a household. By connecting a switch to this router you get more network ports.
The speed of a switch is the most important thing to consider when purchasing. Gigabit ethernet is 10 times faster than fast ethernet. The purchase price is often about the same. Hence, make sure to buy a gigabit switch.
Difference managed and unmanaged
An unmanaged switch is a simple switch without additional settings or advanced functions. This is sufficient for most households.
More can be configured on a managed switch (often through the browser), such as Quality of Service (QoS), VLANs, Access Control Lists (ACLs), monitoring, port configuration, etc.
How this can be configured is always described in the manual.
Difference between switch and router
What does a switch do and how does it work? Switches provide access to the network by providing network ports. Many switches work with so-called ASICS chips. These are programmable chips that provide wire speed. The speed of switches is therefore always higher than routers, because routers work with software instead of chips (hardware).
Routers separate networks. This is, for example, the separation between your home network and the network of your provider. The router ensures that the network traffic is sent (routed) to the correct next 'node': for example another router within the network of your provider.